Ficus hispida
No common name set
EditMoraceae

Main specimen
Habit
Ficus hispida is a medium sized deciduous tree that grows up to 10 m in height.
It is covered with stiff hair or bristles, from which its name "hispid" derives.
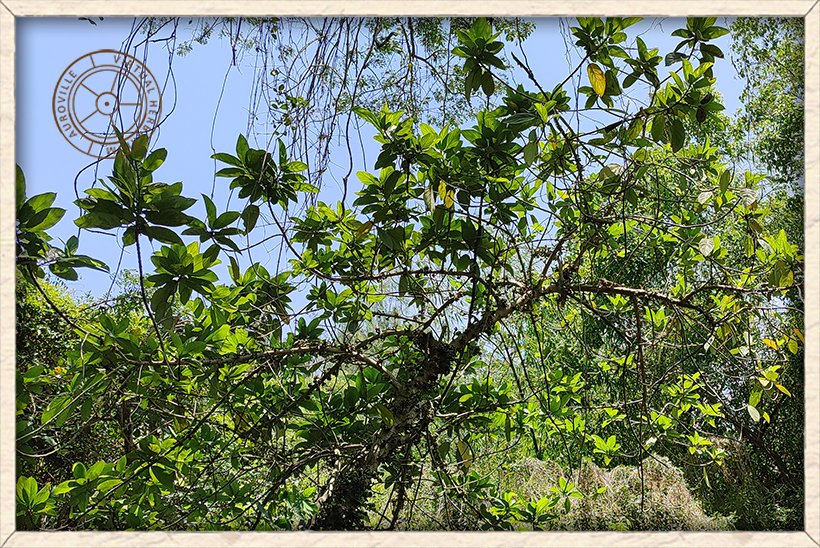

Ficus hispida habit with clusters of figs on the main stem
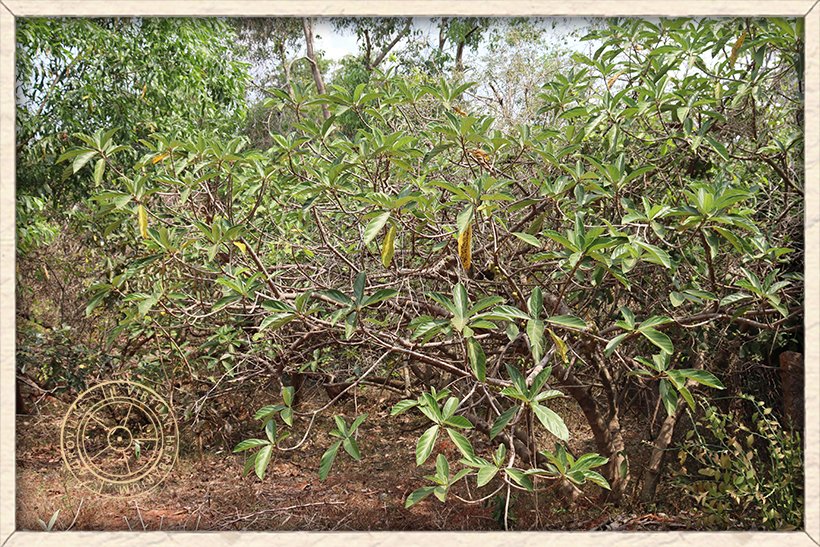

Ficus hispida habit

Ficus hispida habit
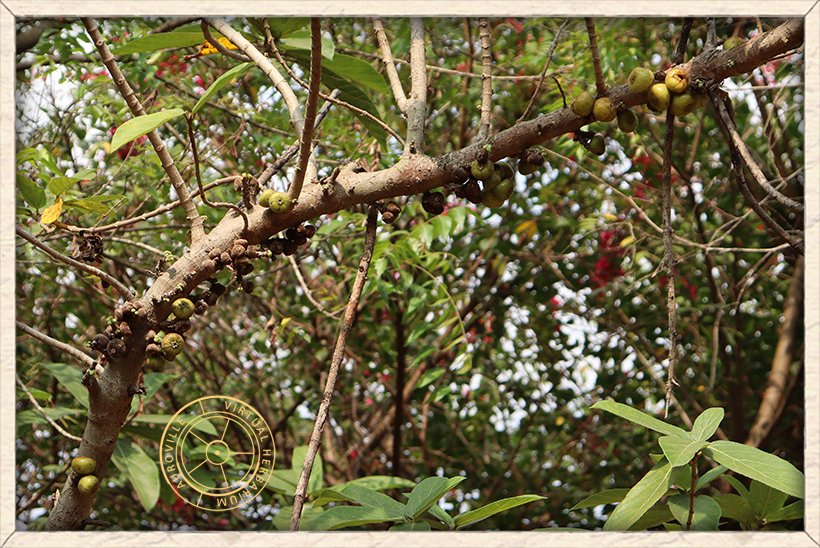

Ficus hispida main stem with clusters of figs on the main stem
Stem Bark
The bark of Ficus hispida is grey and smooth, with light brown lenticels.
The branches are lax.
The twigs and stems exude an abundant milky latex when broken.
The branchlets are terete, with hollow internodes, densely hispid with brown or grey hairs and with lenticels.

Ficus hispida grey smooth bark

Ficus hispida light grey bark, smooth with brown lenticels

Ficus hispida main stem

Ficus hispida hairy brown petiole

Ficus hispida hairy brown branchlet with prominent internodes

Ficus hispida hairy brown leaf attaches on branchlet

Ficus hispida hollow hairy brown internode
Leaf
The leaves of Ficus hispida are simple and grow in a decussate arrangement, often in unequal pairs.
The leaves are oblong to elliptic-lanceolate, they are approximately 10 to 20 cm long and 6 to 10 cm wide.
Like a number of Ficus, both sides of the leaves are coriaceous, sandpapery to touch.
The base of the leaf is rounded, often unequal, and 3-nerved.
The lower side of the leaf has a prominent midrib.
The leaf margin is entire and sometimes minutely toothed.
The petiole is 4 cm long and has a sub-nodal gland.

Ficus hispida leaves

Ficus hispida decussate leaves

Ficus hispida young growth of leaves

Ficus hispida leaf attachement on the stem

Ficus hispida leaf (upper side)

Ficus hispida leaf (lower side)

Ficus hispida leaf (lower side) with prominent midrib and nerves
Flower
The flowers of Ficus hispida are found in the fig itself which is a modified inflorescence with tiny flowers contained inside the fig.
The male flowers are numerous in 1 or 2 whorls.
They have only 1 stamen and short filaments.
The female flowers are sessile or stalked.
The ovary is depressed-globose shaped.
The gall flowers are similar but larger and distinctly stalked.
The figs appear fascicled on the trunk or on elongated pendulous or trailing leafless branches.
The figs are hairy.
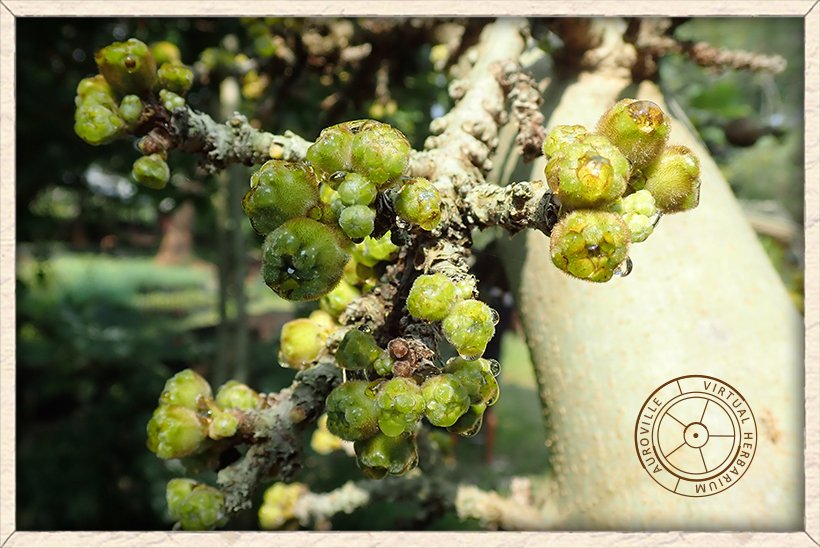

Ficus hispida clusters of hairy figs (the flowers are contained inside the fig)
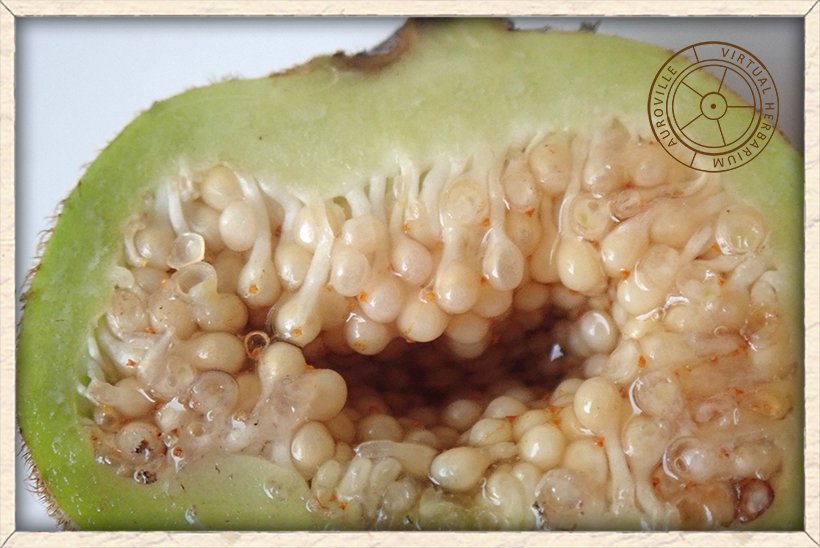

Ficus hispida hairy fig dissected in half to show the flowers

Ficus hispida fig dissected in half to show the flowers
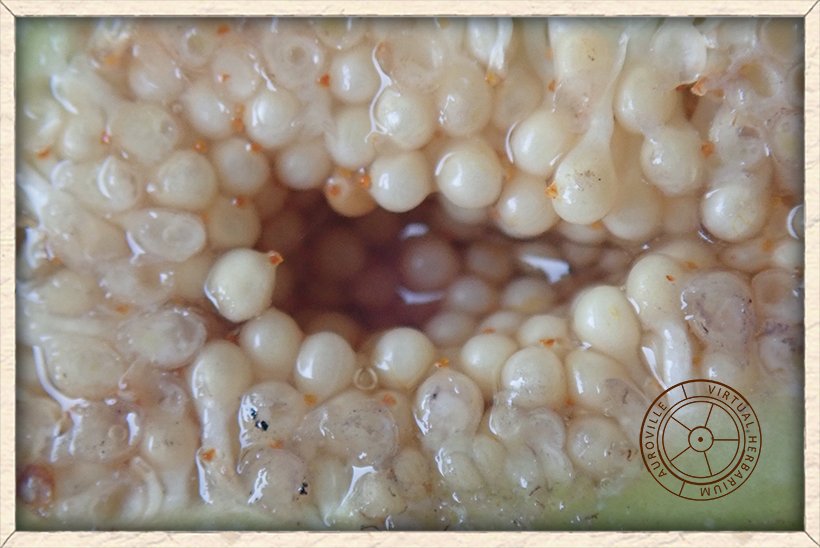
Ficus hispida flowers inside the fig
Fruit
The fruits of Ficus hispida are the figs also known as synconium (or synconia in plural).
The figs appear fascicled on the trunk or on elongated pendulous or trailing leafless branches, often produced in clusters found down to the ground.
An unusual feature is that the figs hang on long stems.
They are disk-like or top-shaped.
The figs are covered in rough and sticky hairs.
They are yellow when ripe, 1 to 3 cm in diameter.
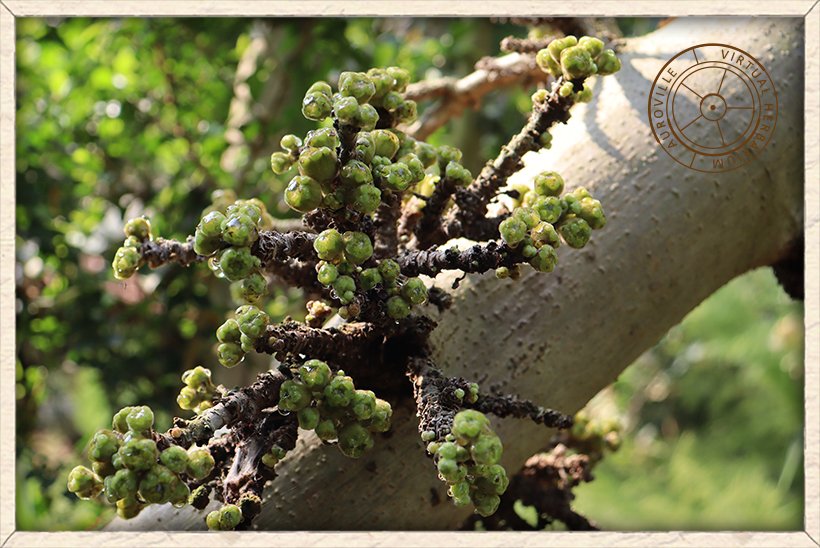

Ficus hispida clusters of figs on the trunk

Ficus hispida clusters of hairy figs found on the trunk
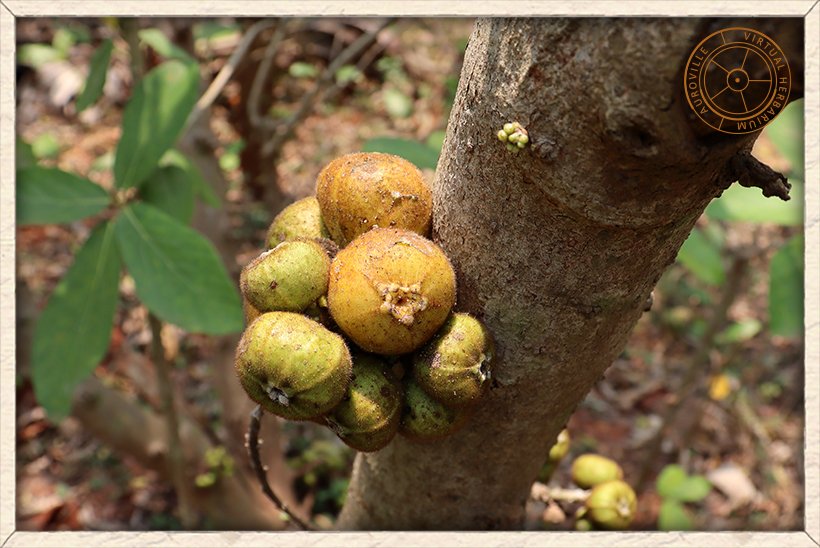

Ficus hispida clusters of figs showing the ostioles for the fig wasp to enter and pollinate them

Ficus hispida clusters of figs on the ostiole side

Ficus hispida fig cut in half showing the inside of the synconium
Seed
The seeds of Ficus hispida are enclosed inside the fig.
It is an achene: a small, dry one-seeded fruit that does not open to release the seed.
The seeds are tiny, about 1 mm in size.
They are grey to light brown in colour.

Ficus hispida hairy figs containing the seeds, lower side (left) and upper side (right)

Ficus hispida fig cut in half, with immature seeds inside

Ficus hispida seeds washed and dried
Source
Information on this page is sourced from: