Canavalia cathartica
No common name set
EditFabaceae

Main specimen
Habit
Canavalia cathartica is a woody and deciduous climber. It is a thornless vine with thick, twining and climbing stems (to 8 meters).
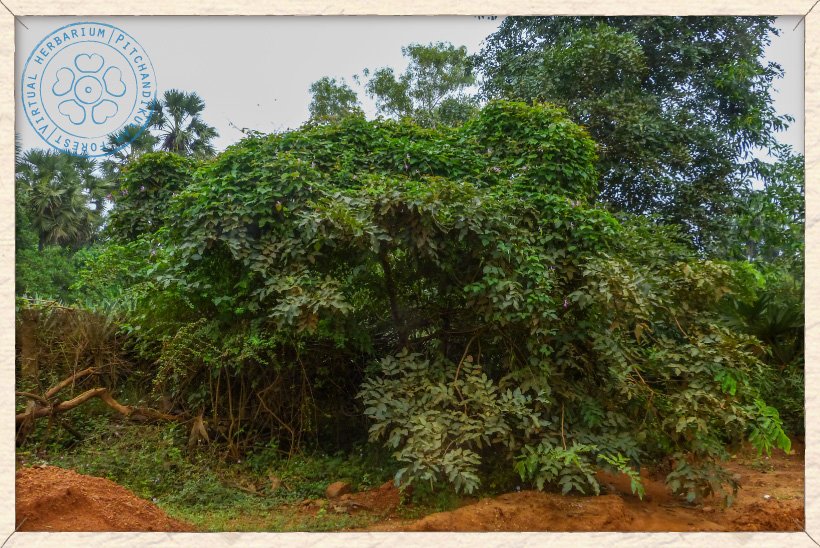

Canavalia cathartica covering shrubs and trees
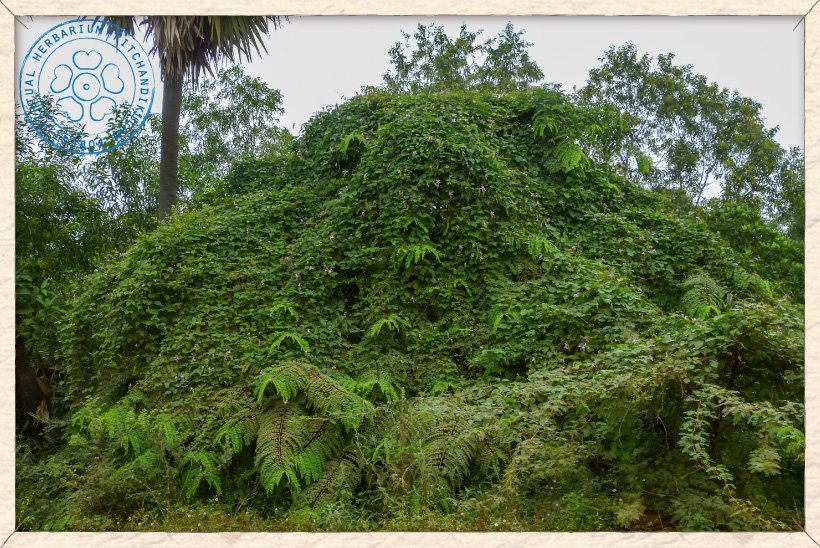

Canavalia cathartica straggling over a tree (Cassia roxburghii)
Stem Bark
The bark of Canavalia cathartica is warty and old stems show vertical veins. The branchlets are glabrous.
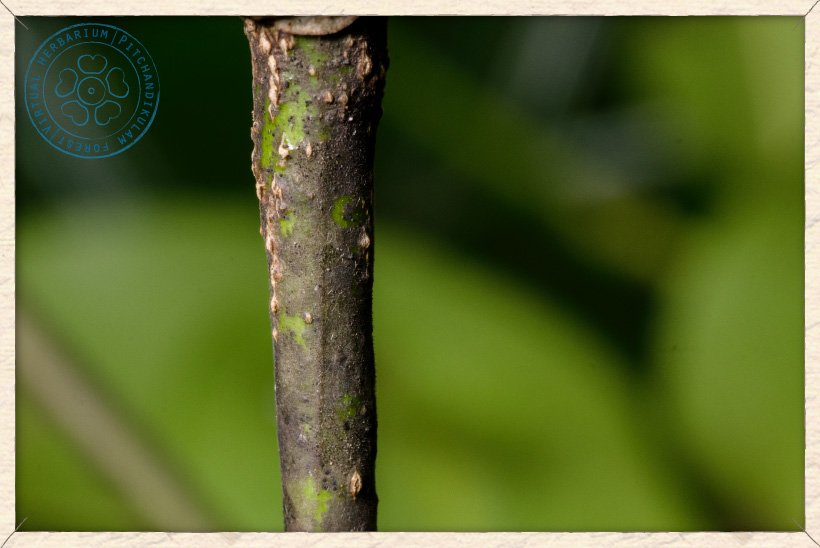

Canavalia cathartica stem and bark
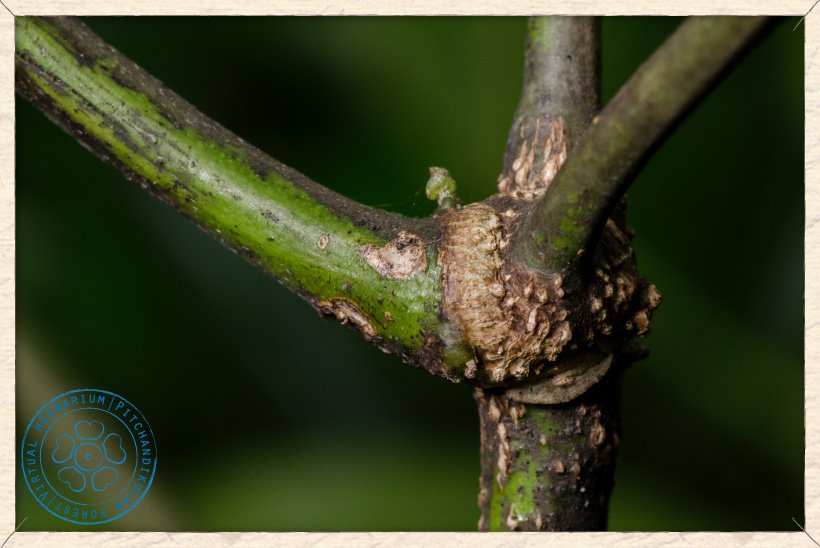

Canavalia cathartica stem node
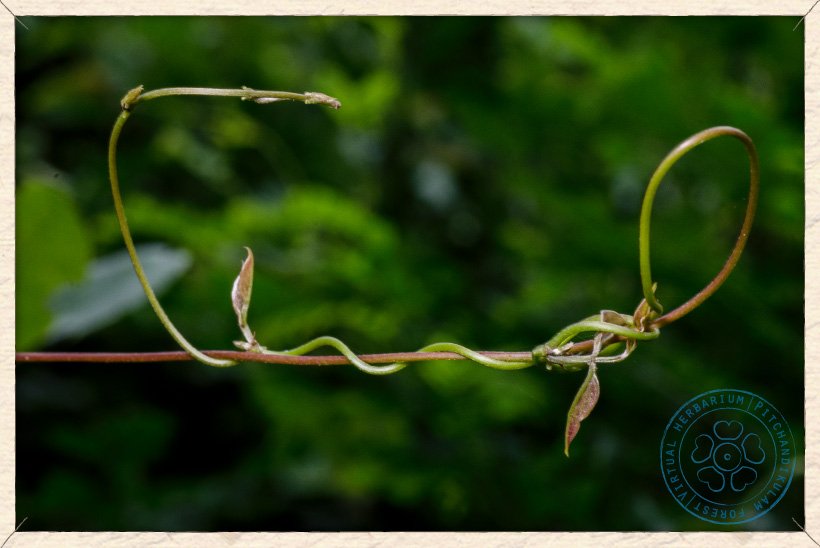

Canavalia cathartica twining shoot
Leaf
Canavalia cathartica has 10 to 20 cm long compound (trifoliolate) and alternate leaves.
The petiole is 5 to 10 cm long.
The leaflets are ovate and 5 to 12 cm long and 2.5 to 8 cm wide. These leaflets are chartaceous with entire margins, acuminate at apex, rounded at base, glabrous above and slightly puberulous below (yellowish-brown coloured hairs).
The petiolules are about 5 mm long. The stipules are subulate and 2-3 mm long.
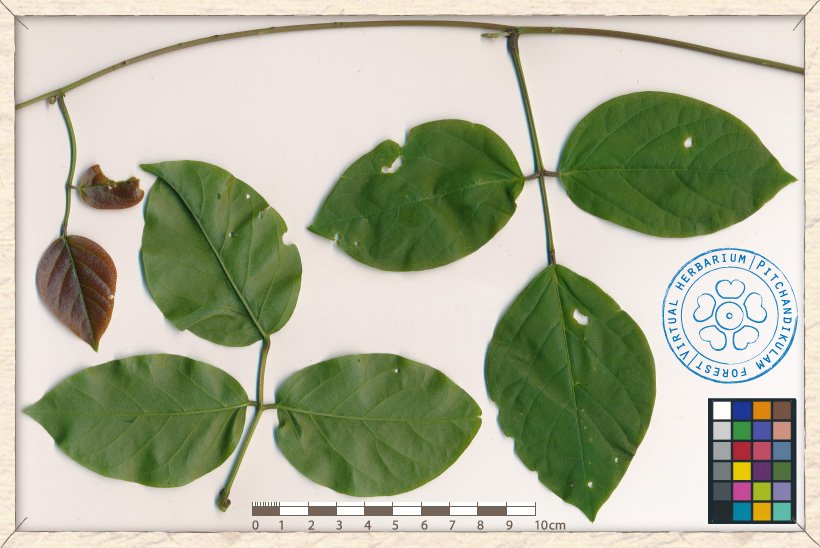

Canavalia cathartica trifoliate leaves
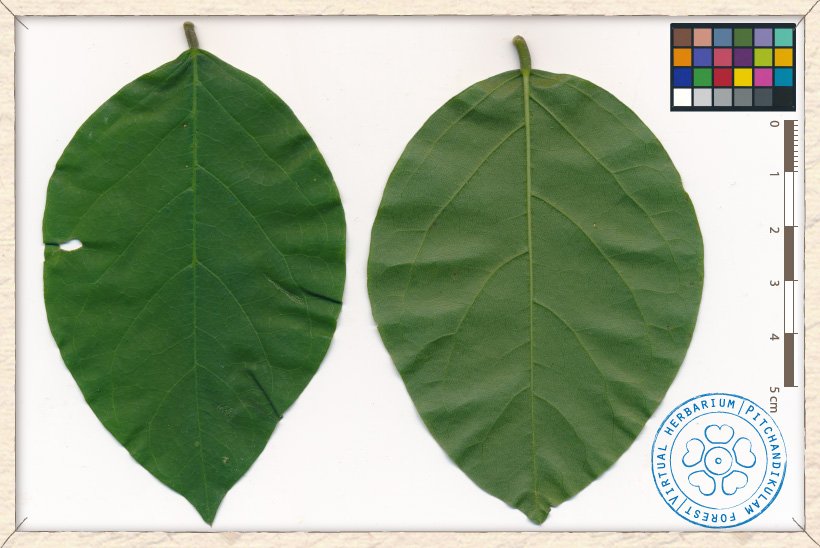

Canavalia cathartica leaflet (upper and lower sides)
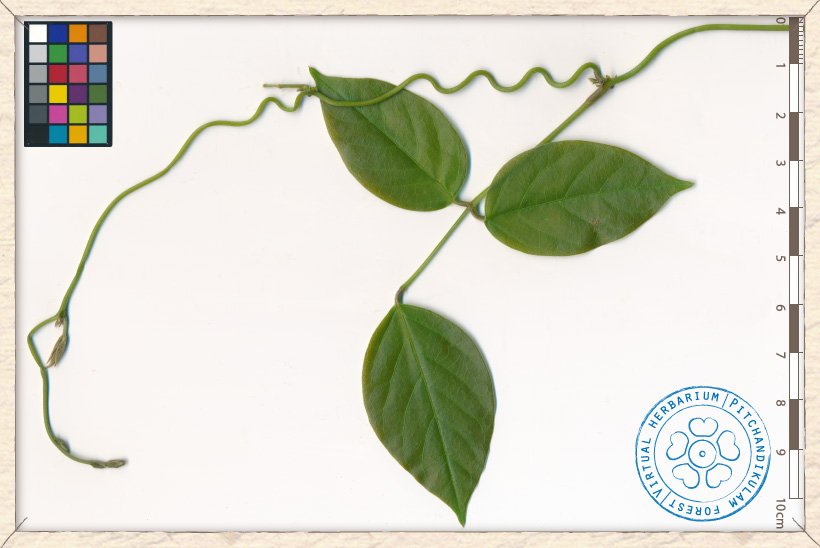

Canavalia cathartica young leaf and twining shoot
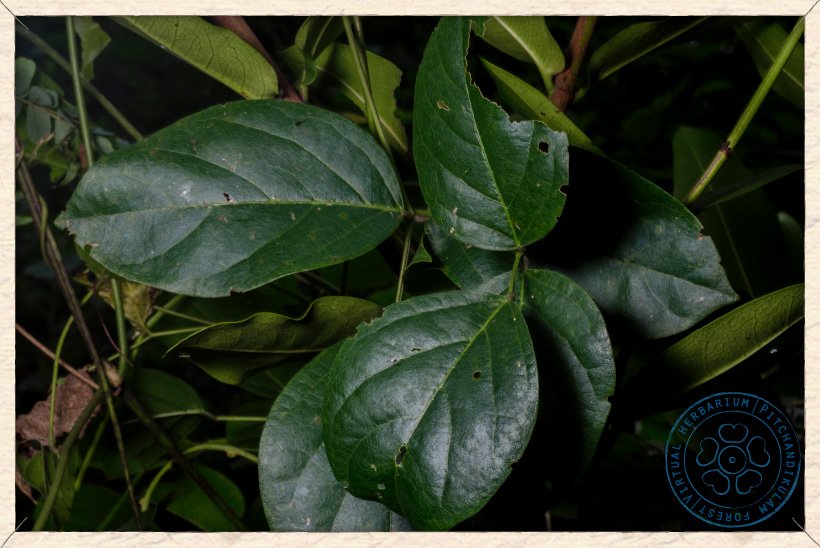

Canavalia cathartica leaf
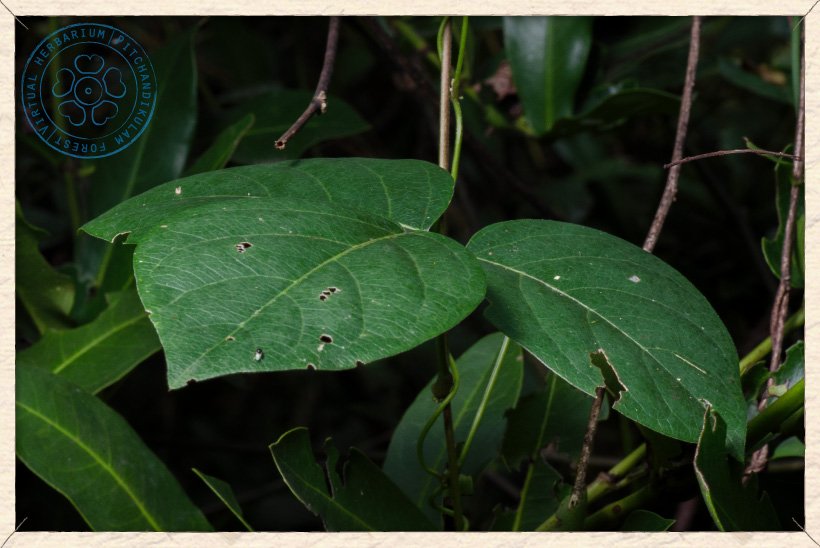

Canavalia cathartica leaf
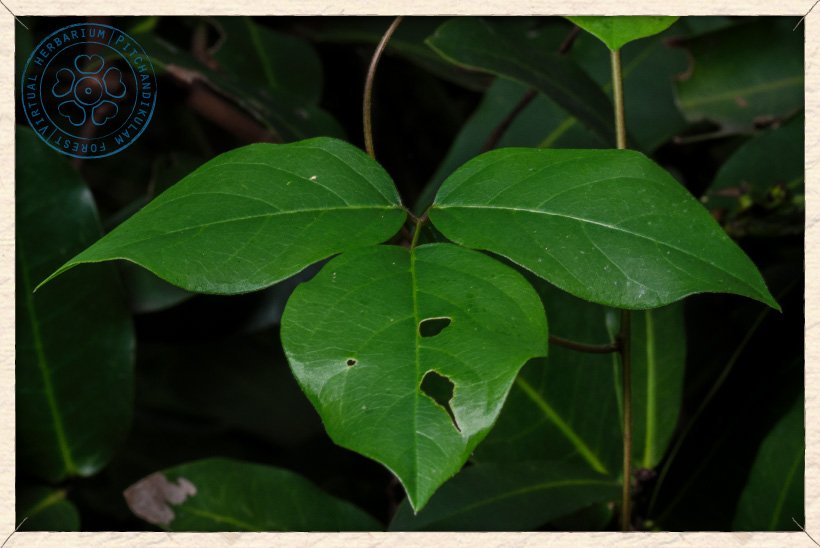

Canavalia cathartica young leaf
Flower
The flowers of Canavalia cathartica are pink, in 10 to 20 cm long axillary racemes.
The peduncle is about 15 cm long and the pedicel of each flower is 3-4 mm long. Both are sparsely hairy.
The flower is 2.5 cm across. The calyx-tube is 1.3-1.5 cm long and 0.5-0.8 cm wide. This tube is 2-lipped : the upper is 2-lobbed (5 mm long) and the lower is 3-dentate (1-2 mm long). The corolla is pink and lilac-coloured. It is composed of a 2x2.5 cm reflex standard, 2 narrow wings (2 cm long and 0.6 cm wide) and 2 incurved keels (2.5 cm long and 0.7 cm wide).
The staminal shealth is 2.5 cm long with 6-8 filaments (0.6-0.7 mm long) and 2 mm long anthers.
The style is curved and about 2.5 cm long and the ovary is about 0.5 cm across with many ovules.
The flowers are fragrant.
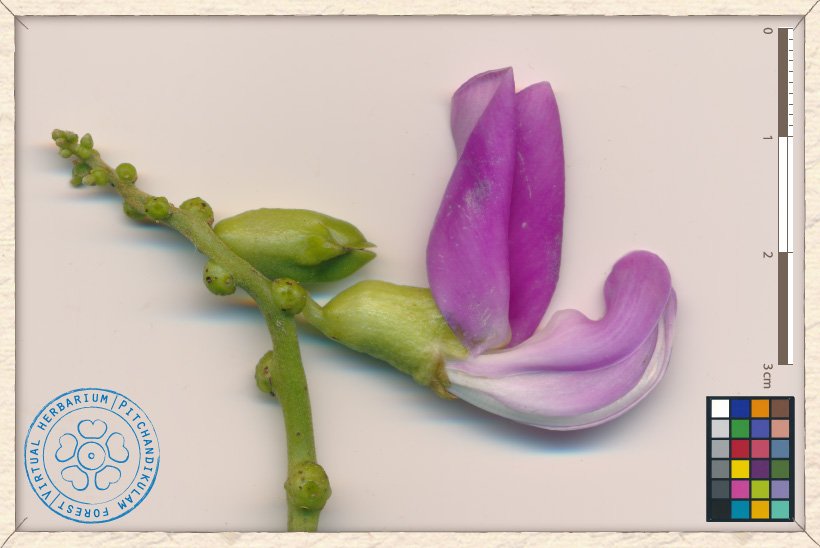

Canavalia cathartica raceme with open flower and bud
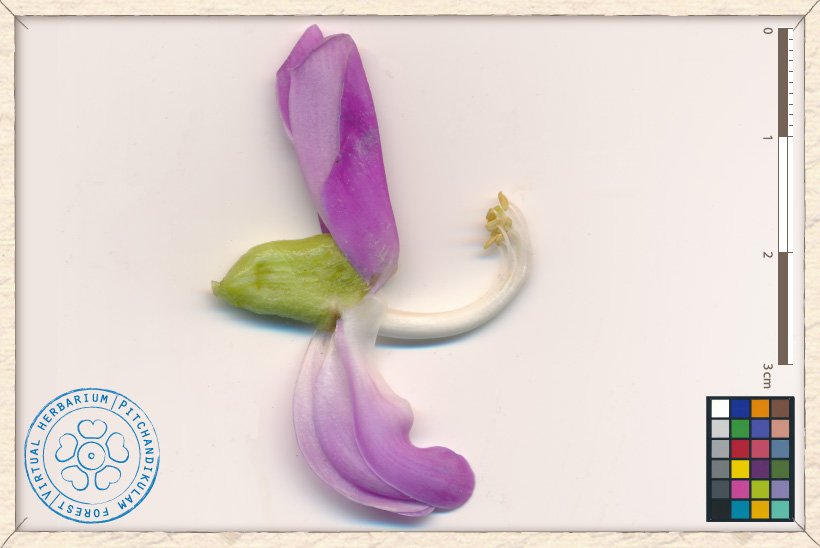

Canavalia cathartica flower
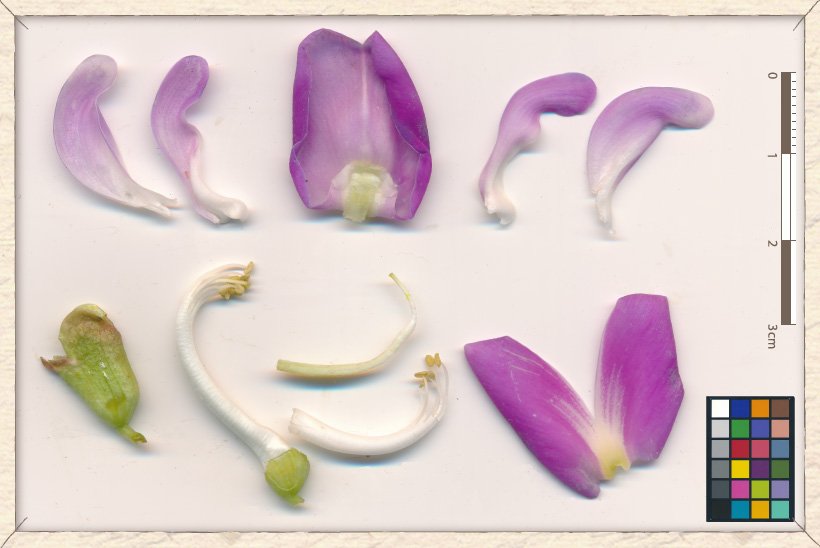

Canavalia cathartica flower parts (sepals, calyx-tube and reproductive structures)
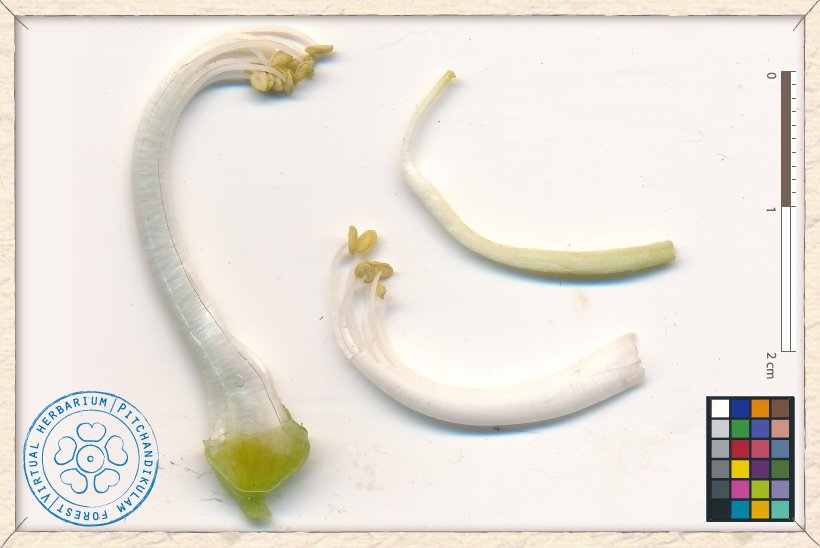

Canavalia cathartica reproductive structures
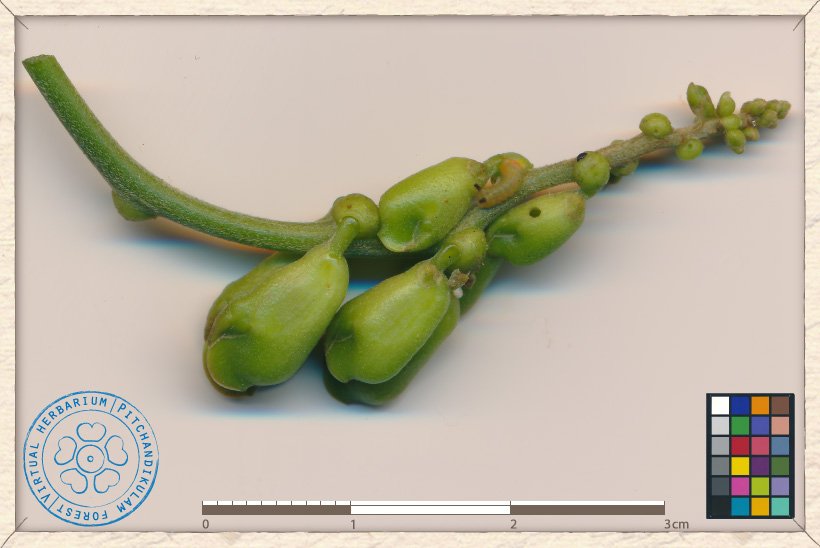

Canavalia cathartica buds
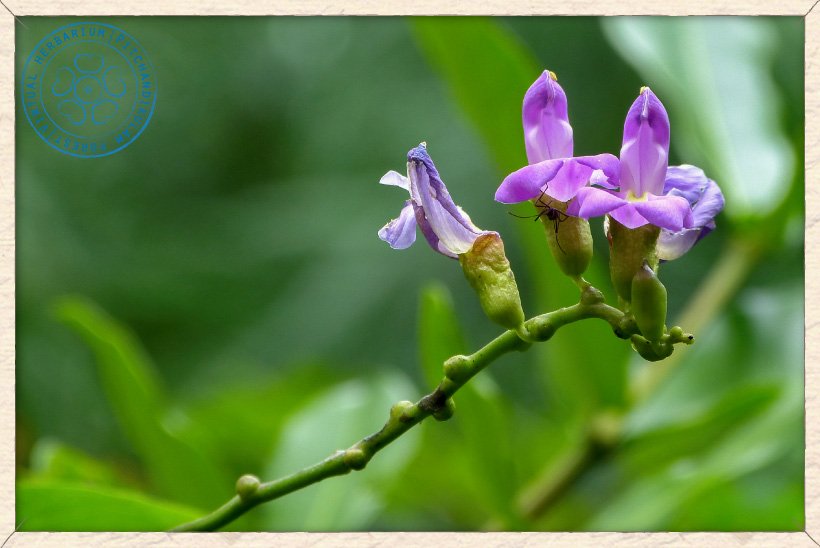

Canavalia cathartica inflorescence
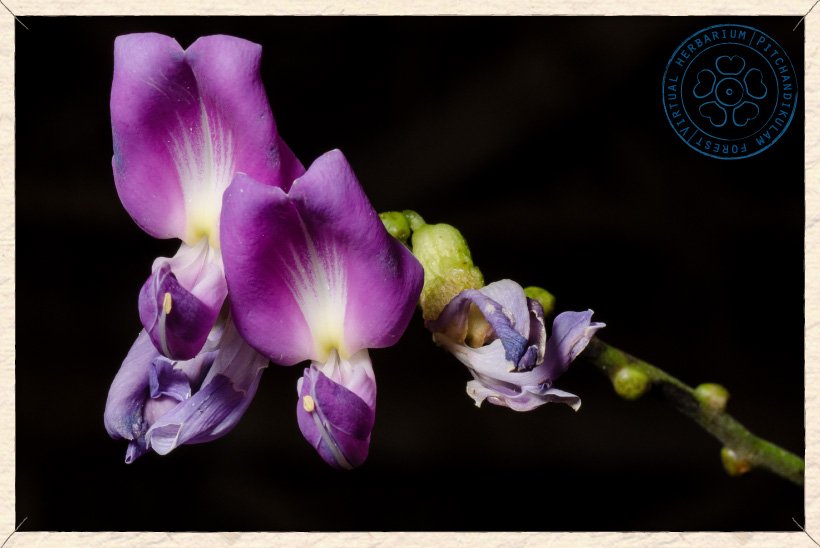

Canavalia cathartica flowers
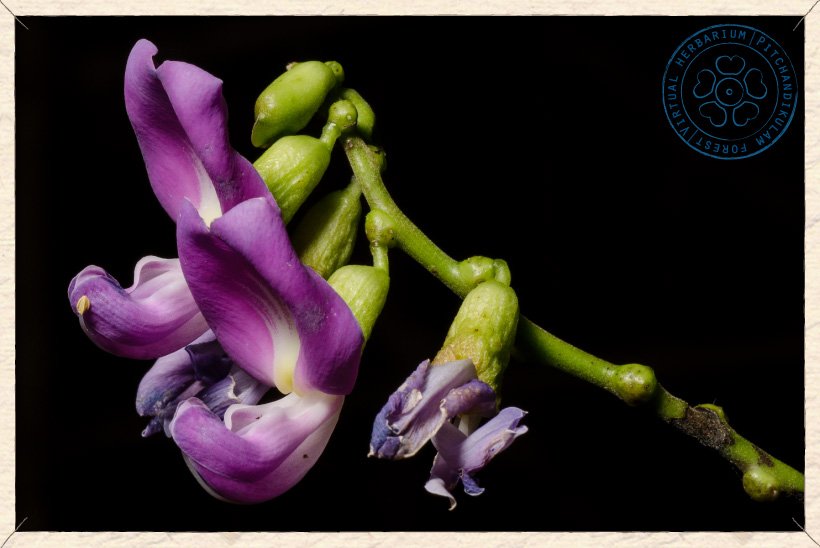

Canavalia cathartica flowers
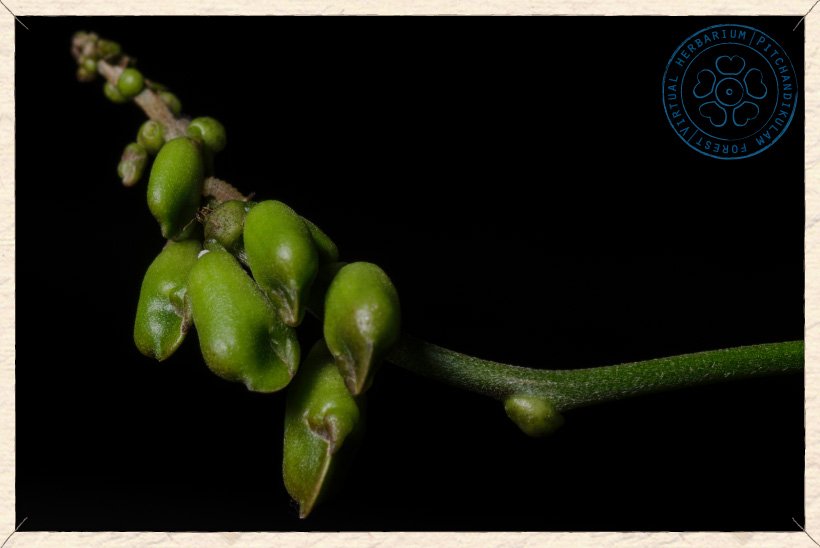

Canavalia cathartica buds
Fruit
The fruit of Canavalia cathartica is a pod.
The thick pod is 10 to 15 cm long and 2 to 2.5 cm wide.
It is oblong, compressed and pubescent with obtuse and horned apex.
The pod is 5-12-seeded and has a 0.5-0.7 cm peduncle.
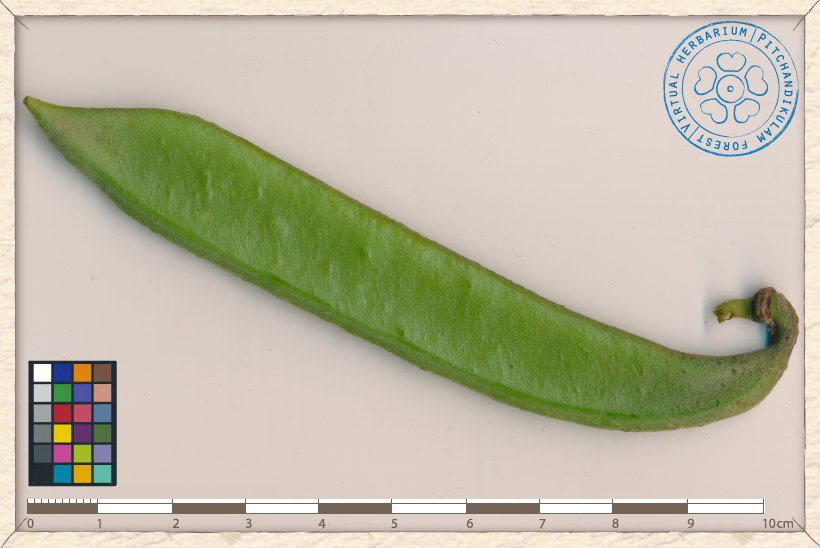

Canavalia cathartica unripe fruit
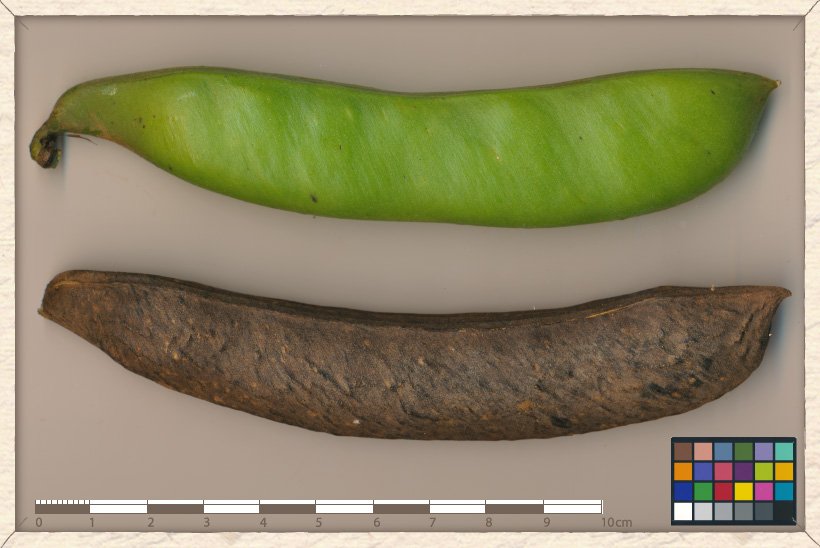

Canavalia cathartica unripe and ripe pods
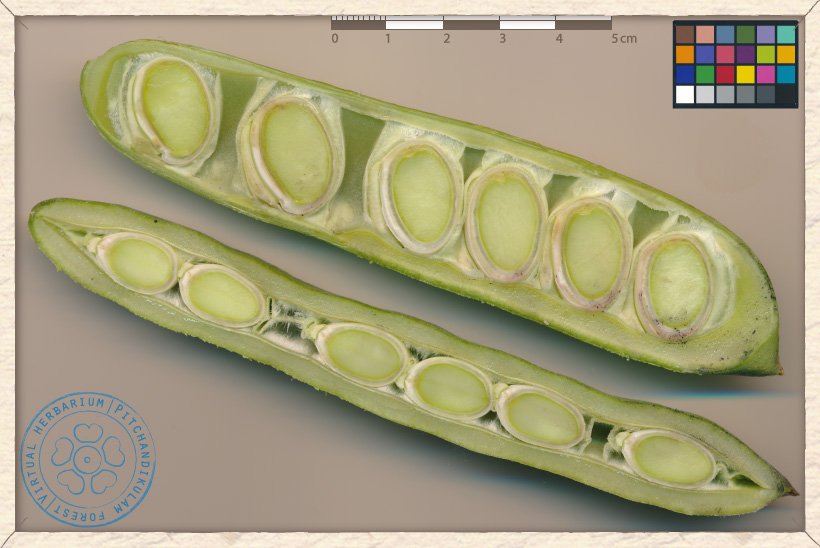
Canavalia cathartica unripe pod longitudinal sections
Seed
Each pod of Canavalia cathartica contains 6 to 12 seeds.
The seeds are smooth, glabrous and 1.5 to 1.8 cm long and 1 cm wide.
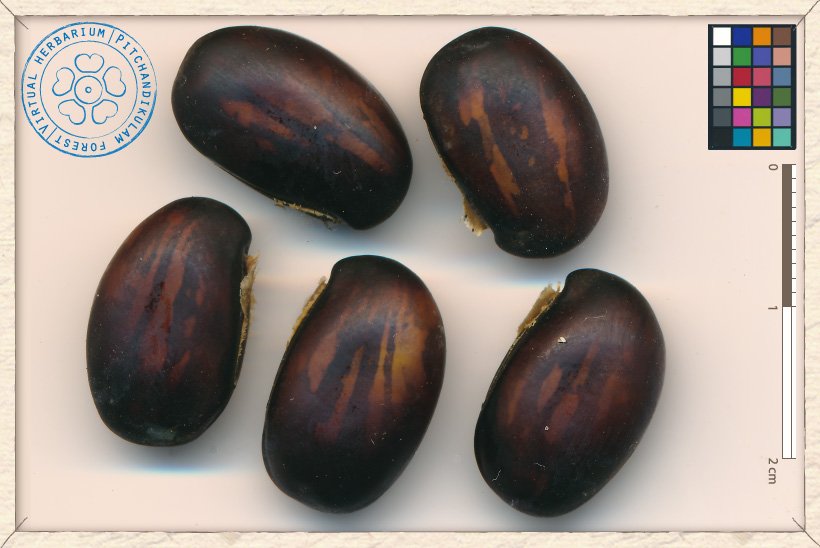

Canavalia cathartica seeds
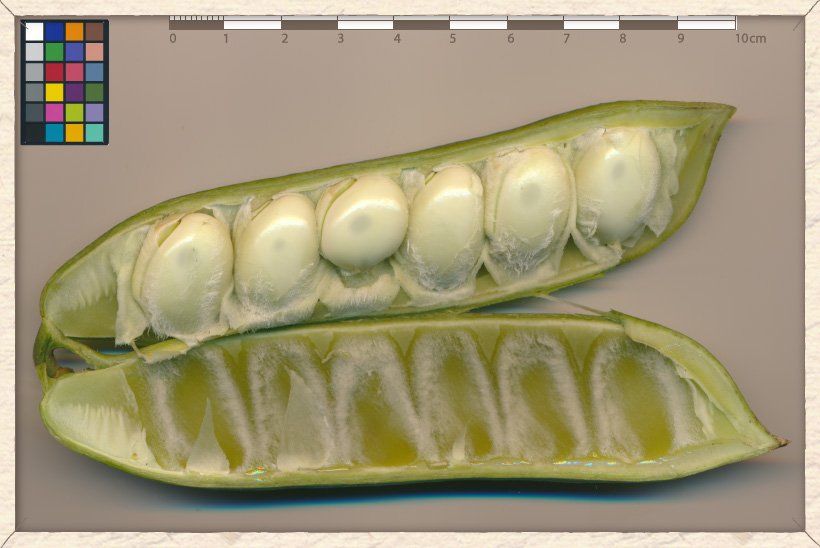
Canavalia cathartica unripe seeds
Human Uses
Canavalia cathartica is used as cattle fodder. The stems with pods and leaves are fed to rabbits and hares. (B. Bhagya, K.R. Sridhar and S. Seena)
In some islands, the showy flowers and large seeds of Canavalia cathartica are used in leis*. (R. Barboza)
* A lei is a wreath of flowers or other objects such as shells, nuts, and feathers, worn especially around the neck.
There are several direct and indirect uses of different parts of Canavalia cathartica throughout the tropical regions of the world.
In India, inhabitants of Karnataka and Kerala consume seeds and immature pods of Canavalia cathartica during shortage of food. Fishermen communities eat cooked immature pods occasionally after removing the fibres.
The seeds of Canavalia cathartica are a rich source of proteins, sulphur and essential amino acids, carbohydrates and energy.
It is considered to be an underutilized wild plant with the potential to serve as a protein and carbohydrate rich food crop. (Nutritional and microbiological features of little known legumes, Canavalia cathartica Thouars and C. maritima Thouars of the southwest coast of India, S. Seena and K. R. Sridhar)
The tender pods are rich in protein, fiber, starch, potassium, magnesium, zinc and manganese and Canavalia cathartica has more protein than several other edible legumes such as pigeon pea, chickpea, and cowpea. (Biochemical and protein quality evaluation of tender pods of wild legume Canavalia cathartica of coastal sand dunes, B. Bhagya, K.R. Sridhar and S. Seena).
The raw, uncooked seeds are narcotic and poisonous but the trypsin inhibitor activity was absent in tender pods and pressure-cooking decreased the other antinutritional factors.
Like many legumes, Canavalia cathartica contains antinutrients and requires some processing or preparation before it can be used for food. Antinutrients in the species include phenols, tannins, and lectins. Pressure cooking can reduce antinutrients. (B. Bhagya, K.R. Sridhar and S. Seena)
Source
Information on this page is sourced from: